Transport in the Democratic Republic of the Congo
Logistics and Transportation in the DR Congo. Waterways. National Roads

The Land transport in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (Central Africa) has always been difficult. The terrain and climate of the Congo Basin are serious obstacles for Road and Railway construction; the distances are enormous in this vast country.
The Democratic Republic of the Congo has thousands of kilometres of waterways and, traditionally, the water transport has been the main transport mode in two-thirds of the Congo.
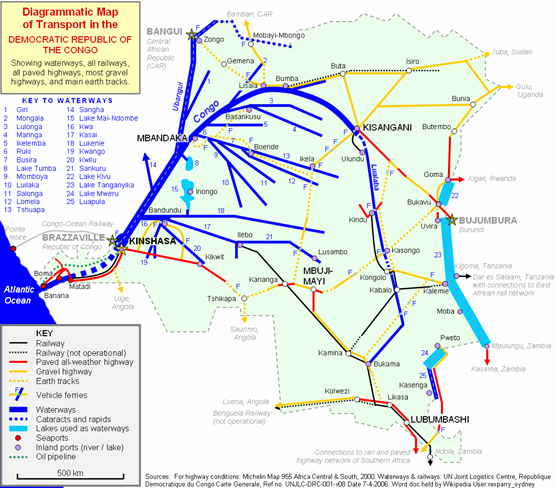
The «National Congolese Route» is used to transport goods to Bukavu from the Port of Matadi, consists of:
- Matadi - Kinshasa - railway
- Kinshasa - Kisangani - riverboat
- Kisangani - Ubundu - railway
- Ubundu - Kindu - riverboat
- Kindu - Kalemie - railway
- Kalemie - Kalundu (Lake Port in Uvira) - boat on Lake Tanganyika
- Kalundu - Bukavu - road
Certain parts of the DR Congo are more accessible from neighboring countries than from Kinshasa.
- For example, Bukavu, Goma and other north-west cities are connected by paved road from the border of the DR Congo to the Port of Mombasa in Kenya.
- Lubumbashi and the rest of Katanga province are linked to Zambia
Dolisie (Republic of the Congo, Niari department): 140 kilometres north-west of the border (Central Kongo)
- National Route (Rwanda) 3b: Butare (Lake Kivu, border of the DR Congo, route to Bukavu)
- National Route (Rwanda) 4: Kigali (Lake Kivu, border of the DR Congo, route in Goma)
Seaports
- Port of Matadi is the largest port, and the start line for the railway to Kinshasa
- The second largest port is Boma
- Port of Banana (Atlantic Ocean), oil terminal, a pipeline to Kinshasa
- Provinces of the South of the Congo: Port of Walvis Bay (Namibia, Trans-Caprivi corridor)
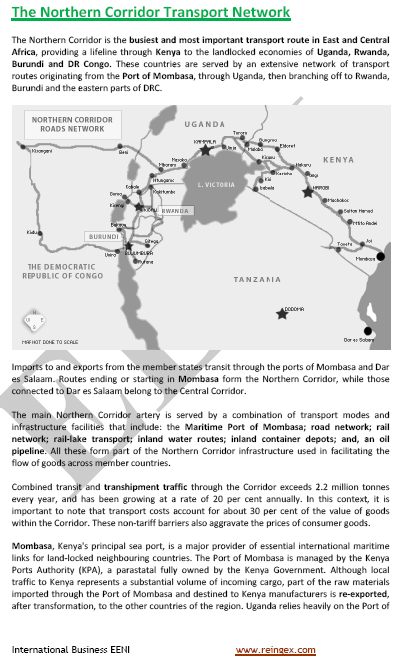
- Eastern provinces of the DR Congo: Port of Mombasa (Kenya)
Other nearby ports:
- Angola (Cabinda):
- Republic of the Congo: Port of Pointe-Noire
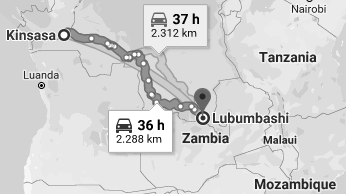
- Mozambique: Port of Beira (Lubumbashi, 1,600 kilometres)
- Tanzania: Port of Dar es Salaam
Distance from Lubumbashi to Kinshasa: 2,288 kilometres (36 hours)
Road network is divided into four categories (national roads, priority regional roads, regional secondary roads and local roads). The two main roads are:
- National Road No. 1 that connects the Atlantic seaports with Kinshasa and South-East of Katanga, the most important economic zone of the country due to its copper mines
- National Road n. ° 2, Kisangani-Bukavu-Goma, which links the main river systems of the country, namely Kinshasa-Kisangani on the Congo River and the Lake Kivu and Lake Tanganyika systems on the eastern end of the Congo.
Three roads of the trans-African road network cross the Democratic Republic of the Congo:
- Tripoli-Windhoek Transport Corridor: this route crosses the western end of the Congo on National Road No. 1 between Kinshasa and Matadi, at a distance of 285 kilometres, is one of the only paved sections in good condition
- Lagos-Mombasa Transport Corridor: the Democratic Republic of the Congo is the main stretch to finish this road
- Beira-Lobito Transport Corridor: this east-west route crosses Katanga, but needs a major reconstruction:
Others corridors:
- Lobito Transport Corridor
- Northern Transport Corridor
- North-South Transport Corridor
- Central Transport Corridor
Rail transport in the DR Congo is managed by the National Society of the Congolese Railways (SNCC). All railway lines are not connected but are generally connected by river transport.
Congo River (4,700 kilometres)
- Kinshasa is the largest African River port
- Kinshasa-Kisangani route of 1,000 kilometres on the Congo River is the longest and most used
- Malebo Pool (Kinshasa and Brazzaville)
- Congo Basin: 3,700,000 km²
- Source of the Congo: Lwalaba (Katanga)
- Tributaries: Oubangui and Kasaï
- Kinshasa and other river ports on the Ubangui River Bangui (Central African Republic)
- Rubber and Bukavu on Lake Kivu in Gisenyi, Kibuye and Cyangugu in Rwanda.
- Kalemie, Kulundu-Uvira and Moba on Lake Tanganyika in Kigoma (Tanzania), Bujumbura (Burundi) and Mpulungu (Zambia).
- Kasenga and Pweto on the network of the Luapula-Lake Mweru River in Nchelenge, Kashikishi and Kashiba in Zambia.
 Congo
Congo
- Course: Transport and Logistics in Africa
- Masters: Business in Africa, Transport and Logistics in Africa
- Doctorate in African Business

More information: International Trade and Business in the DR Congo, at EENI Global Business School Website.
 Transporte en la RD Congo
Transporte en la RD Congo
 Transport en RD Congo
Transport en RD Congo
 Transporte na RD Congo
Transporte na RD Congo


 Tweet
Tweet