Foreign Trade and Transport in Burundi, Bujumbura
Business in Burundi, Bujumbura, Muyinga, Ruyigi. Coffee. Corridors

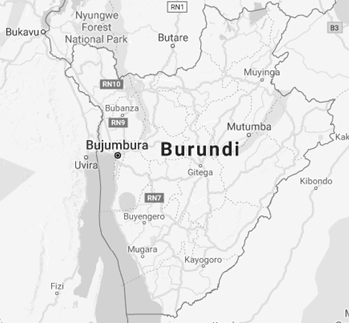
Burundi is a landlocked country of Central Africa / Eastern Africa
- Burundi belongs to the Great Lakes region (Lake Tanganyika)
- Bujumbura is the economic, political and administrative capital of Burundi and the largest Burundian city
- The largest cities of Burundi are Bujumbura, Muyinga, Ruyigi, Gitega, Ngozi, Rutana. Bururi, Makamba, Kayanza and Muramvya
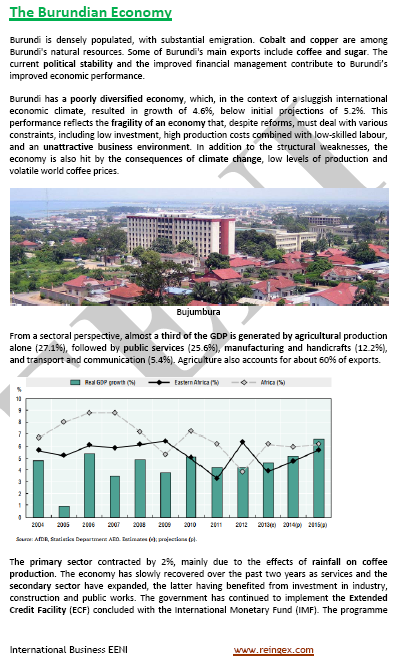
- Burundi is a resource-poor country with an underdeveloped manufacturing sector.
- The main economic activities in Burundi are agriculture (50% of the GDP of Burundi), transport, tourism and cattle raising
- The main export products of Burundi are coffee (80% of the Burundian exports), tea and cotton
- The main natural resources of Burundi are uranium, nickel, cobalt, copper and platinum.
- The leading industries in Burundi are assembly of imported components, construction, public works, food processing and light consumer goods (blankets, shoes and soap).
- Burundi is one of the eight poorest countries in the world
- Currency of Burundi: Burundian Franc (BIF)
- Burundi has borders with the DR Congo (233 kilometres), Rwanda (290 kilometres) and Tanzania (451 kilometres)
 Burundian Students
Burundian Students


More information: International Trade and Business in Burundi, at EENI Global Business School Website.

Transport and Logistics in Burundi
Bujumbura International Airport is the only airport with a paved runway
Transport network of Burundi is limited and underdeveloped. Burundi has a road network, but less than 10% of the country's Roads are paved
Bujumbura connects with Kigoma, Tanzania, for a passenger and freight ferry (MV Mwongozo).
There is a long-term plan to connect Burundi by rail to Kigali and then to Kampala (Uganda) and Kenya.
- National Route 3 of Rwanda: Kigali - Gitarama - Butare -Fugi (the border of Burundi, the route towards Bujumbura)
- National Route 5 of Rwanda: Kigali - Nyamata - border of Burundi (route towards Kirundo).
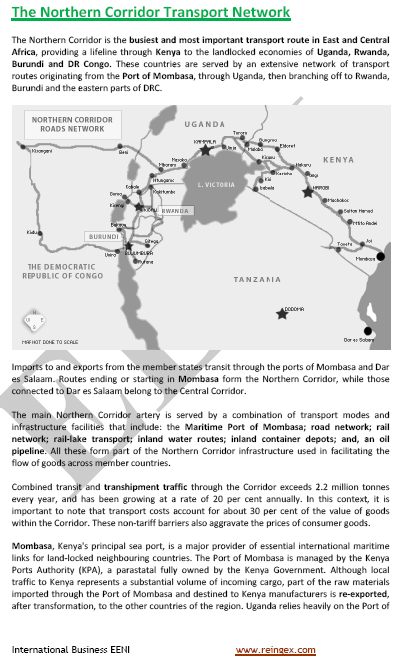
Transafrican Transport Corridors:
- Northern Transport Corridor (Uganda, Burundi and Rwanda, Mombasa - Kenya Sea Port)
- Central Transport Corridor
- Burundi, the DR Congo, Rwanda, Tanzania and Uganda
- Burundian population: 11 million inhabitants
- Burundi is a mostly rural society, only 13% of the population lives in urban areas
- Climate of Burundi: temperate equatorial
- Heha Bujumbura Mountain: 2,670 meters
- Area of Burundi: 27,834 km²
- Population density of Burundi: 398.8 inhabitants/km²
- Burundi is one of the smallest countries in continental Africa
- Burundi is a multi-party Republic with a presidential regime
- Republika y'Uburundi in Kirundi language
- Burundi obtained its Independence from Belgium in 1962
- Calling code of Burundi: 257
- Burundian code top-level domain: .bi
- National Parks: Kibira and Ruvubu
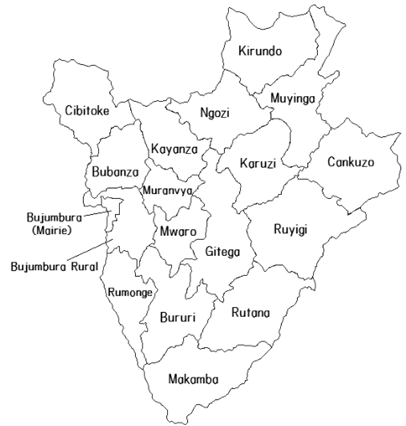
The 18 provinces of Burundi are:
- Bubanza
- Bujumbura Mairie
- Bujumbura Rural
- Bururi
- Cankuzo
- Cibitoke
- Gitega
- Karuzi
- Kayanza
- Kirundo
- Makamba
- Muramvya
- Muyinga
- Mwaro
- Ngozi
- Rumonge
- Rutana
- Ruyigi
The largest Burundian cities are:
- Bujumbura
- Muyinga
- Ruyigi
- Gitega
- Ngozi
- Rutana
- Bururi
- Makamba
- Kayanza
- Muramvya

Trade and Business Organisations (Burundi)
- Economic Community of Central African States (ECCAS)
- Common Market for Eastern and Southern Africa (COMESA)
- U.S.-COMESA Agreement
- East African Community (EAC)
- United States-East African Community (EAC) Agreement
- COMESA-EAC-SADC Agreement
- Economic Community of the Great Lakes Region
- Nile Basin Initiative
- Conference on the Great Lakes Region
- Organisation for the Harmonisation of Business Law in Africa (OHADA)
- International Organisation of the Francophonie
- African Development Bank
- African Union
- AUDA-NEPAD
- Economic Commission for Africa
Main Burundian ethnicities:
85% of the Burundian population is Hutu ethnic origin, 15% are Tutsi, and less than 1% are Twa (indigenous).

Religions and Global Business -
Religious diversity
Religions in Burundi:
-
Christianity
- Catholicism (62% of the Burundian population)
- Protestantism (22% of the Burundian population)
- African Traditional Religions
Languages of Burundi
The official languages of Burundi are Kirundi (97% of the population), French (10% of the Burundian population) and English (from 2014)
History of Burundi
Twa, Hutu and Tutsi have lived in Burundi for at least 500 years. During more than 200 of those years, Burundi was an independent Kingdom, until the beginning of the 20th century, when Germany colonized the region.
- 16th century: the Kingdom of Burundi. The King: Mwami
- 17th century: first conflicts between ethnic groups
- Middle of the 18th century: consolidation of Tutsi royalty
- 1903: German East Africa
- 1915: Belgian colonial empire
- 1962: independence (Belgium)
- 1970 - 1980: conflicts between Tutsi and Hutu
- 1972: a dictatorial regime of President Micombero (Tutsi)
- Hutu Insurrection, 100,000 Hutu dead
- 1993: Burundian civil war
- In October 1993, Tutsi soldiers killed Ndadaye, an act that sparked a genocide against the Tutsi, which led to years of violence between the Hutu rebels and Tutsi majority army. 300,000 people, mostly civilians, died in the years after the murder.
- 2001: new Constitution (concept of ethnic power alternation).
Higher Education in Burundi
LMD System (Bachelor, Master, Doctorate) - Ministry of Education, Science, Technology and Scientific Research
- University of Burundi (Bujumbura)
- University Hope Africa (Bujumbura)
- University of the Lake Tanganyika
Burundi is a member of


 Tweet
Tweet

