Foreign Trade and Transport in the Central African Republic
Business in the Central African Republic (Ködörösêse tî Bêafrîka), Bangui, Bimbo, Mbaiki, Berbérati

The Central African Republic (CAR) is a Central African country
- Bangui is the political, economic and administrative capital of the Central African Republic
- Other largest Central African cities are Bimbo (Ombella-M'Poko), Mbaiki (Lobaye), Berbérati (Mambéré-Kadéï), Kaga Bandoro, Bozoum, Carnot, Sibut, Bambari and Bria.
- The Central African Republic is a developing country
- Agriculture represents 50% of the GDP of the Central African Republic
- Main products manioc, corn, coffee, cotton, bananas and tobacco
- Main Central African natural resources: oil, uranium, gold and diamonds
- The Central African Republic is a landlocked country (without access to the sea)
- The headquarters of the Economic and Monetary Community of Central Africa (CEMAC) are in Bangui
- Central African Republic = Ködörösêse tî Bêafrîka in Sango
- Currency of the Central African Republic: CFA Franc (XAF)
- The Central African Republic share borders with Cameroon (Garoua, Ngaoundéré), Chad, the Republic of the Congo, the DR Congo, Sudan (175 kilometres) and South Sudan.

Transport and Logistics in the Central African Republic
The Central African Republic is a landlocked country, which implies some important costs for its exports.
- The port of Douala (Cameroon, 1,500 kilometres) is the main international trade port of the Central African Republic
- Port of Douala (Congo) - Congo-Ocean Railway and waterway

Bangui is the logistics centre of the Central African Republic.
In the Central African Republic, the road condition is too degraded
- National Road 1 (482 kilometres): Bangui, Bossangoa, Moundou (Chad).
- National Road 2 (1,202 kilometres): Bangui, Bambari. Bangassou a Bambouti (border of Sudan)
- National Road 3 (453 kilometres): Bossembélé, Bouar, Baboua,
Garoua-Boulai (border of Cameroon).
- Transafrican Corridor Lagos-Mombassa
- Corridor Douala-Bangui.
- National Road 4 (554 kilometres): Damara, Bouca, Batangafo to Sarh (Chad).
- National Road 5: Bambari, Ippy, Bria, Ouadda, Birao
- National Road 6 (605 kilometres): Bangui, Mbaïki, Carnot, border of Cameroon (Berbérati, Gamboula)
- National Road 7 (87 kilometres): Bossemptélé - Bozoum
- National Road 8: Kouango, Ongo, Sibut, Kaga-Bandoro, Ndélé, Birao (border of Sudan).
- National Road 9: Kongbo, Mobaye
- National Road 10 (136 kilometres): Berbérati, Bania, Nola.
- National Road 11 (104 kilometres): Baoro, Carnot
- Bangui M’poko Airport.
- No rail transport in the Central African Republic
- River route through the Congo and the Oubangui rivers
 Central Africa
Central Africa


More information: International Trade and Business in the Central African Republic, at EENI Global Business School Website.

Trade and Business Organisations (Central African Republic)
- Central African Economic and Monetary Community (CEMAC)
- Economic Community of Central African States (ECCAS)
- OHADA
- Community of Sahel-Saharan States (CEN-SAD)
- Bank of Central African States (BEA)
- OIF

- African Union
- AUDA-NEPAD
- Economic Commission for Africa
- African Development Bank

- The Central African Republic obtained its Independence from France in 1960 (French colony of Oubangui-Chari)
- Calling code: 236
- Code top-level domain: .cf
- Places of interest:
- Megaliths of Bouar (UNESCO World Heritage)
- Cathedral of Notre-Dame of Bangui
- Berengo Palace
- Central African population: 5.1 million inhabitants
- 1975: 2 million
- Population density of the Central African Republic: 8.3 inhabitants/km²
- Area of the Central African Republic: 622,984 km²
- Climate of the Central African Republic: tropical
- Most of the Central African Republic consists of a Sudan-Guinean savannas
- The Central African Republic also includes a Sahelo-Sudanese area in the north and an area of equatorial forest in the south.
- Two thirds of the country is in the Ubangi river basin (which flows into the Congo River), while the remaining third is in the Chari basin, which empties into the Lake Chad.
The ten main cities of the Central African Republic (city/prefecture) are:
- Bangui/Bangui
- Bimbo, Bégoua/Ombella-M'Poko
- Berbérati/Mambéré-Kadéï
- Carnot/Mambéré-Kadéï
- Bambari/Ouaka
- Bouar/Nana-Mambéré
- Bria/Haute-Kotto
- Bossangoa/Ouham
- Nola/Sangha-Mbaéré
- Bangassou/Mbomou
Prefectures of the Central African Republic
The prefectures of the Central African Republic are (in brackets: capital) are:
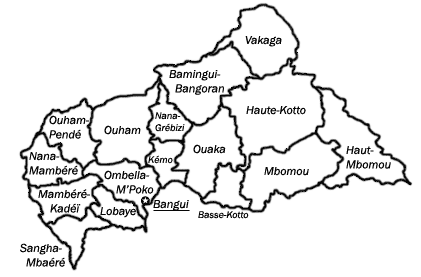
- Bamingui-Bangoran (Ndélé)
- Basse-Kotto (Mobaye)
- Haute-Kotto (Bria)
- Haut-Mbomou (Obo)
- Kémo (Sibut)
- Lobaye (Mbaïki)
- Mambéré-Kadéï (Berbérati)
- Mbomou (Bangassou)
- Nana-Mambéré (Bouar)
- Ombella-M'Poko (Bimbo)
- Ouaka (Bambari)
- Ouham (Bossangoa)
- Ouham-Pendé (Bozoum)
- Vakaga (Birao)
Main Central African ethnicities:
In the Central African Republic there are more than 80 ethnic groups, each with its own language.
The most important ethnic groups are Baya-Mandjia (50% of the population), Banda (40%), Mandjia, Sara, Mboum, M'Baka (7%), Yakoma, Fula...

Religions and Global Business -
Religious diversity
Religions in the Central African Republic:
-
Christianity (80% of the population)
- Protestantism (51%)
- Catholicism (29%)
- Islam (10%)
- African Traditional Religions
Languages of the Central African Republic
In the Central African Republic there are more than 100 languages: Sango, Banda of the South, Banda-banda, Bokoto, Gbanou, Gbaya of North-West and South-West...
The official languages of the Central African Republic are French and Sango (vehicular language, 93% of the Central African speak Sango)
Only a small part of the population of the Central African Republic has a basic knowledge of French, the official language.
History of the Central African Republic
- Ninth millennium BC: carved stones (Pygmy?)
- Third millennium BC: Bantu expansion and populations of the Adamaoua-Ubangi group
- Pygmy marginalisation
- 700-1376: Kanem Empire
- 15th century: Zandé expansion
- Kingdoms Zandé
- 18th - 19th centuries: Slave Trade. Strong demographic regression
- Ndélé: Slavery centre (Sultan of Baguirmi)
- Dar el-Kouti: Slave state
- Conversion to Islam
- 18th century: the Ngbandi create the Central African vernacular language: Sango
- 1522-1897: Kingdom of the Baguirmi
- 1635-1912: Ouaddaï Empire
- 1889: construction of Bangui
- 1905: French colony of Oubangui-Chari, French Equatorial Africa (1910)
- 1960: Independence (France). Barthélemy Boganda
- 1965: Saint-Sylvestre coup d'état, Jean-Bedel Bokassa
- 1974: Authoritarian regime of Jean-Bedel Bokassa (emperor)
- 1979: French operation (Barracuda). David Dacko
- 1981: General André Kolingba (military regime).
- 1993: free elections (multiparty). President Ange-Félix Patassé
- 2003: President François Bozizé
- Two civil wars
- 2014: cessation of hostilities, agreement in Brazzaville.
Higher Education in the Central African Republic
LMD System (Bachelor of Science-Master-Doctorate)- Ministry of Higher Education of the Central African Republic
- University of Bangui (public university)
The Central African Republic is a member of:
 República Centroafricana
República Centroafricana
 République centrafricaine
République centrafricaine
 República Centroafricana
República Centroafricana


 Tweet
Tweet