Foreign Trade and Transport in the Republic of the Congo
Business in the Republic of the Congo, Pointe-Noire, Brazzaville, Petroleum, Business

The Republic of the Congo (Congo-Brazzaville) is a Central African country
- Brazzaville is the political and administrative capital of the Republic of the Congo and the largest Congolese city (2 million inhabitants)
- Pointe-Noire (715,000 inhabitants) is the economic capital of the Republic of the Congo
- Dolisie (Niari) is the third largest Congolese city (100,000 inhabitants)
- Other Congolese cities are Nkayi (Bouenza), Impfondo (Likouala), Ouésso (Sangha), Madingou (Bouenza), Owando (Cuvette), Sibiti (Lékoumou), Loutété (Bouenza)
- The Congo river delimit the border between the DR Congo and the Republic of the Congo
- The Congo River is the second river in the world by the average flow
- The Republic of the Congo is:
- The fourth African oil producer (Pointe-Noire, 90% of the Congolese exports)
- The largest African potash producer
- Tropical jungle: 66% of the Congolese territory
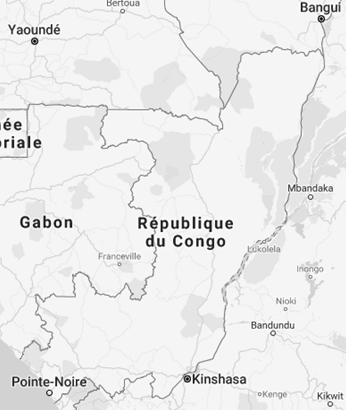
- The Republic of the Congo share borders with Angola (Cabinda), Cameroon (523 kilometres), Gabon (1,903 kilometres, Upper Ogooué, Franceville, Oyem), the Central African Republic (Bimbo, Mbaiki) and the DR Congo (Congo river, Ubangi River)

Transport and Logistics in the Republic of the Congo
The port of Pointe-Noire: access to the countries of the Congo Basin:
- Central African Republic (Bangui): waterway and Railway
- Chad (N'Djamena): waterway and railway
- Cameroon
- Gabon
- Angola
- DR Congo

Other Congolese ports:
- Brazzaville (Congo river)
- Impfondo (Congo river)
- Ouesso (river Sangha)
Paved Roads in the Republic of the Congo: 1,000 kilometres
National Congolese road network:
- N1 Brazzaville - Kinkala - Dolisie - Pointe-Noire
- N2 Brazzaville - Owando - Ouésso
- N3 Dolisie - border with Gabon
Road to Gabon (Moanda, 100 kilometres)
Access to the Corridor Tripoli-Congo-Windhoek Transport Corridor.
Congo-Ocean Railway: links Brazzaville with the port of Pointe-Noire (502 kilometres)
- Access to the Central African Republic (Bangui) by the Ubangi River
Waterways: Congo and Oubangui rivers provide 1,120 km of Waterways
Maya-Maya International Airport and Pointe-Noire Airport



More information: International Trade and Business in the Republic of the Congo, at EENI Global Business School Website.

- Congolese population: 5.1 million inhabitants
- Population density of the Republic of the Congo: 13 inhabitants/km²
- 62% of the Congolese population is urban, concentrated in Brazzaville and Pointe-Noire
- Area of the Republic of the Congo: 342,000 km²
- The Republic of the Congo has 220 kilometres of coastline in the Atlantic Ocean
- The Republic of the Congo obtained its Independence from France in 1960
- 1969 - 1992: the Republic Popular of the Congo
- Calling code of the Republic of the Congo: 242
- Code top-level domain of the Republic of the Congo: .cg
- Currency of the Republic of the Congo: CFA Franc (XAF)
- Congolese climate: warm and humid
Théophile Obenga (Congolese historian)

Departments of the Republic of the Congo
The departments of the Republic of the Congo (department, capital, population in thousands of people, area in km²) are:
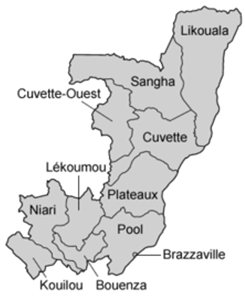
- Kouilou/Hinda/92/13,650. Districts:
- Hinda
- Madingo-Kayes
- Mvouti
- Kakamoéka
- Nzambi
- Tchiamba-Nzassi
- Niari/Dolisie/231/25,942. Districts:
- Louvakou
- Kibangou
- Divénié
- Mayoko
- Kimongo
- Moutamba
- Banda
- Londéla-Kayes
- Makabana
- Mbinda
- Moungoundou-South
- Nyanga
- Moungoundou-North
- Yaya
- Lékoumou/Sibiti/96/20,950. Districts:
- Sibiti
- Komono
- Zanaga
- Bambama
- Mayéyé
- Bouenza/Madingou/309/12,265. Districts:
- Madingou
- Mouyondzi
- Boko-Songho
- Mfouati
- Loudima
- Kayes
- Kingoué
- Mabombo
- Tsiaki
- Yamba
- Pool/Kinkala/236/33,955. Districts:
- Kinkala
- Boko
- Mindouli
- Kindamba
- Goma Tsé-Tsé
- Mayama
- Ngabé
- Mbanza-Ndounga
- Louingui
- Loumo
- Ignié
- Vindza
- Kimba
- Plateau/Djambala/174/38,400. Districts:
- Djambala
- Lékana
- Gamboma
- Abala
- Allembé
- Makotimpoko
- Mbon
- Mpouya
- Ngo
- Ollombo
- Ongogni
- Cuvette/Owando/156/48,250. Districts:
- Owando
- Makoua
- Boundji
- Mossaka
- Loukoléla
- Oyo
- Ngoko
- Ntokou
- Tchikapika
- Cuvette-West/Ewo/73/26,600. Districts:
- Ewo
- Kellé
- Mbomo
- Okoyo
- Etoumbi
- Mbama
- Sangha/Ouesso/86/55,800. Districts:
- Mokéko
- Sembé
- Souanké
- Pikounda
- N’gbala
- Likouala/Impfondo/154/66,044. Districts:
- Impfondo
- Epéna
- Dongou
- Bétou
- Bouanéla
- Enyellé
- Liranga
- Brazzaville/1,373/100
- Pointe-Noire/715/44
Urban communes of the Republic of the Congo:
- Dolisie
- Nkayi
- Mossendjo
- Ouesso
- Owando

Trade and Business Organisations (Republic of the Congo)
- Central African Economic and Monetary Community (CEMAC)
- Economic Community of Central African States (ECCAS)
- OHADA
- Bank of Central African States (BEA)
- OIF
- African Union
- AUDA-NEPAD
- Economic Commission for Africa
- African Development Bank
Main Congolese ethnicities:
In the Republic of the Congo, there are several ethnic groups, each with its language.
The most important ethnic groups of the Republic of the Congo are:
- Kongo: 48% of the Congolese population
- Sangha: 20%
- Téké: 17%
- M’Bochi: 12%

Religions and Global Business -
Religious diversity
Religions in the Republic of the Congo:
-
Christianity (50% of the Congolese population)
- Catholicism (33% of the Congolese population)
- Protestantism
- African Traditional Religions (48% of the Congolese population)
Languages of the Republic of the Congo
The official language of the Republic of the Congo is French (spoken by 56% of the Congolese population)
The national vehicular languages (Bantu) of the Republic of the Congo are:
- Kituba (Munukutuba, Kikong Creole), spoken by 50% of Congolese (South of the Congo)
- Lingala (language of the river), spoken in North and East of the Congo
In the Republic of the Congo, there are more than 40 languages: Téké languages (17% of the population; departments: Plateau, Cuvette-West, Niari, Bouenza and Pool), Lari (spoken by Laris, Brazzaville), Pygmy languages...
History of the Republic of the Congo
- First inhabitants of the Republic of the Congo: the Pygmy Mbuti
- Bantu Migrations from the North. Introduction of ironwork
- X-XII centuries: the Kingdom of Loango (in the south, Mayombe massif)
- 15th century: contacts with the Europeans
- Transatlantic Slave Trade
- Thirteenth century: the Kongo (south-east of the Republic of the Congo, North of Angola and Cabinda)
- 17th Century: The Tip Kingdom (East)
- 1875: Pierre Savorgnan de Brazza (France)
- 1883: foundation of Pointe-Noire
- 1885: integration of the Republic of the Congo in the French Equatorial Africa (French colonial empire, capital: Brazzaville)
- 1891: creation of the French Congo colony
- 1960: independence of France. First Congolese Head of State: Fulbert Youlou
- 1963, 1968, 1977 and 1979: coups of state
- 1990: civil war
- Denis Sassou-Nguesso Congolese Head of State (1979 to 1992, 1997 until today)
Higher Education in the Republic of the Congo
LMD System (Bachelor of Science-Master-Doctorate)- Ministry of Higher Education of the Republic of the Congo.
- University Marien Ngouabi (Brazzaville)
- Free University of the Congo (Brazzaville)
- High School of Management and Business Administration (ESGAE) (Brazzaville)
- High School of Technology (Brazzaville)
- High School of Technology of the Littoral (Pointe-Noire)
- Higher Institute of Technology of Central Africa (Pointe-Noire)
The Republic of the Congo is a member of:
 República del Congo
República del Congo
 République du Congo
République du Congo
 República do Congo
República do Congo


 Tweet
Tweet