Bantu People (Central, East, Southern Africa)
The word Bantu means «people» or «human». Ndebele, Shona, Luba, Zulu

Several events in the history of Africa have shaped the current Africa: Sahara desertification, African Islamization, slavery, colonization, or Bantu expansion from the Northern Cameroon. Bantu expansion originated around 2,000 before the common era.
The word Bantu means «people» or «human».
The term Bantu does not refer specifically to an ethnic group or a particular language, but to a set of more than 400 ethnic groups that speak Bantu languages (more than 650 Bantu languages, Nigerian-Congolese languages) that live between Cameroon and Somalia; in Central Africa, East Africa and Southern Africa.
The main countries with significant Bantu groups are:
- South Africa
- Angola
- Botswana
- Burundi
- Cameroun
- Central African Republic
- Comoros
- Equatorial Guinea
- Gabon
- Kenya
- Lesotho
- Malawi
- Mozambique
- Namibia
- Republic of the Congo
- DR Congo (80% of the Congolese population)
- Rwanda
- São Tomé and Príncipe
- Seychelles
- Eswatini
- Uganda
- Tanzania
- Zambia
- Zimbabwe
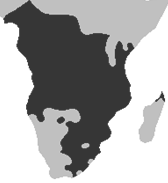
The most important Bantu ethnic groups are:
- Ndebele and Shona, Zimbabwe (14 million people)
- Luba, DR Congo (13 million people)
- Zulu, South Africa (10 million people)
- Sukuma, Tanzania (8 million people
- Kikuyu, Kenya (6 million people)
- Other Bantu ethnic groups are Fang, Bakuba, Baluba, Lingala, Bakongo, Hutu, Baganda, Tonga, Bechuana, Herero, Swazi, Sotho, or Xhosa.

Religions and Global Business -
Religious diversity
The main religion of Bantu are African Traditional Religions, except those Christianised or Islamised groups.
The most important Bantu linguistic groups (300 million people) are Swahili, Zulu (27 million), Sotho, Shona (11 million) or Lingala.
Bantu language with the highest total number of speakers is Swahili; however, the majority (180 million) use it as a secondary language.
Bantu kingdoms
- 14th and 15th centuries: Monomatapa kings (Great Zimbabwe)
- 16th century:
- In Central Africa: the Kingdom of Kongo, Lunda Empire and Luba Empire (Angola, the Republic of the Congo and the Democratic Republic of the Congo)
- In East Africa: Buganda and Karagwe Kingdoms (Uganda and Tanzania)
- In Southern Africa: Mutapa Empire, Rozwi Empire and the Kingdoms of Danamombe, Khami and Naletale (Zimbabwe and Mozambique)

EENI Principle of Racial Harmony



 Tweet
Tweet

