Foreign Trade and Transport in Ghana, Accra, Ashanti
Business in Ghana (second African gold producer), Accra, Cape Coast, Kumasi

Ghana (the first African colony to obtain its Independence) is a West African country (Gulf of Guinea)
- Ghanaian population: 29 million inhabitants
- The capital of Ghana is Accra (2.2 million people). Kumasi
- Ghana has significant oil reserves
- Ghana is the second African gold producer
- Ghana has a universal health system
- Currency of Ghana is the Ghanaian Cedi
- Ghana share borders with Burkina Faso (West-Centre, South-Centre and South-West regions), Ivory Coast and Togo (Kara region); the three countries are Francophone.
Logistics and transport in Ghana

The main ports of Ghana are the ports of Tema and Takoradi
Port of Tema:
- 85% of the Ghanaian International Trade
- 30 kilometres from East of Accra
Port of Takoradi
- Distances from the Port of Takoradi to:
- Accra: 225 kilometres
- Port of Abidjan (Ivory Coast): 300 kilometres
- Gateway to Mali and Burkina Faso
Access to the Railway loop: Benin-Niger-Burkina Faso-Ivory Coast
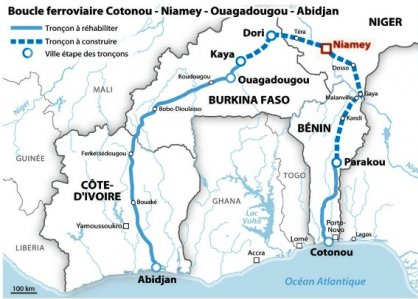
Route: Niamey (Niger), Ouagadougou (Burkina Faso), Ghana
Access to the Dakar-Lagos Transport Corridor
 Ghanaian Students from Ghana
Ghanaian Students from Ghana


 EENI Principle of Racial Harmony (James Emman Kwegyir Aggrey)
EENI Principle of Racial Harmony (James Emman Kwegyir Aggrey)
More information: International Trade and Business in Ghana, at EENI Global Business School Website.

The official language of Ghana is English (67% of the population)
- Ghana is an observer country of the International Organisation of La Francophonie
African languages of Ghana:
- Asante (Akuapem Twi, Asante Twi, Fanti): one of the main languages of Ghana (48% of the population)
- Ewe
- Fanti
- Abron
- Hausa
- Wale (Daggare)
- Dangme
- Ga
- Gonja
- Kasem
- Nzema
- Sokodé
- Total Ghanaian area: 238,540 km²
- Calling code of Ghana: 233
- Country code top-level domain: .gh
- Kwame Nkrumah (pan-Africanist and African leader, Africanisation concept of the administration, 1909-1972)
- The Nobel Peace Prize and former Secretary-General of the UN, Kofi Atta Annan, was born in Kumasi (Ghana) on April 8, 1938
The Ghanaian Historian Albert Adu Boahen Kwadwo (Colonialism in Africa and African contemporary history)

The Republic of Ghana is composed of ten regions, each region is divided into districts. The regions of Ghana are (County capital):
- Ashanti (Kumasi/2 million inhabitants)
- Brong Ahafo (Sunyani)
- Central (Cape Coast)
- Upper East Region (Bolgatanga)
- Greater Accra (Accra)
- North (Tamale)
- Western (Sékondi-Takoradi)
- Eastern (Koforidua)
- Upper West Region (Wa)
- Volta (Ho)


Trade and Business Organisations (Ghana)
- West African Monetary Zone (WAMZ)
- Community of Sahel-Saharan States (CEN-SAD)
- Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS)
- European Union-Ghana Free Trade Agreement
- Global System of Trade Preferences
- African Development Bank
- African Union
- AUDA-NEPAD
- Economic Commission for Africa
Religion in Ghana:
- Christianity: 71% of the Ghanaian population
- Islam: 17%
- African Traditional Religions
Min Ghanaian ethnicities:
- Akans: 47% of the population of Ghana, 11,5 millions in Ghana (8,5 in
Ivory Coast)
- Akans traditional clothing is the pagne kita (kenté) (kenté)
- Akans groups: Bron, Ashanti, Baoulé, Agni, Appolo, Attié, Abbey, Abidji, Adioukrou, Alladian, Abouré, Ebrié, Avikam, Tchokossi, Akuapem, Denkyira, Fanti
- Mole-Dagbani (Dagombas): 17%
- Ewe: 14%
- Ga-Dangme: 7%
- Lobi (North-East, Mossi Diaspora)
- Senufo
Ewe Fetish (African Art Exhibition: “The Animal, A Sacred Symbol”)



 Tweet
Tweet

