Trade and Transport in São Tomé and Príncipe, Port
Business in São Tomé and Príncipe, San António, port, agriculture, tourism and fishing

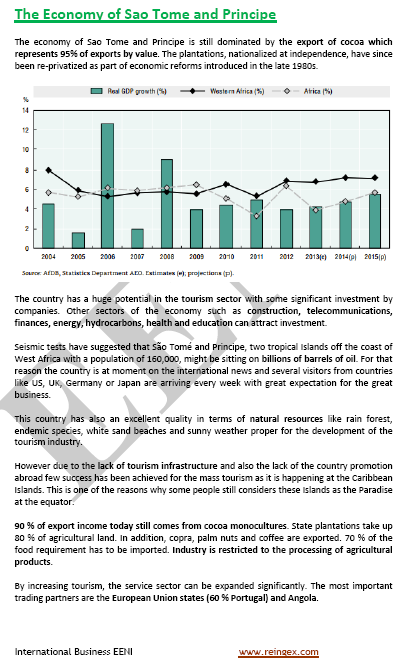
The Democratic Republic of São Tomé and Príncipe is a Central African island country
- Santomean population: 212,000 inhabitants
- São Tomé is the economic, political and administrative capital of São Tomé and Príncipe
- São Tomé is the largest Santomean Port
- Population of São Tomé: 53,000 inhabitants
- Main economic activities: agriculture and fishing
- Significant cacao production
- Main natural resources: hydroelectric power and fishing
- Tourist and oil potential
- The recent discovery of oil deposits in its waters has opened a new perspectives for the future
- São Tomé and Príncipe is a flag of convenience
- São Tomé and Príncipe is one of the poorest African countries
- Santomean economy depends on international aid (50% of the Santomean GDP)
- São Tomé and Príncipe continues to maintain close bilateral relations with Portugal.

Trade and Business Organisations (São Tomé and Príncipe)
- Economic Community of Central African States (CEEAC)
- Community of Sahel-Saharan States (CEN-SAD)
- Bank of Central African States (BEA)
- Community of Portuguese Language Countries (CPLP)

- African Union
- AUDA-NEPAD
- Economic Commission for Africa
- African Development Bank

Religions and Global Business -
Religious diversity
Main Santomean religions:



More information: International Trade and Business in São Tomé and Príncipe, at EENI Global Business School Website.
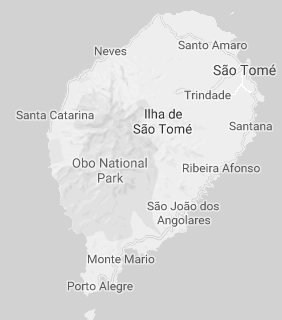
São Tomé and Príncipe is an archipelago in the South Atlantic (Gulf of Guinea) composed of two islands:
- São Tomé:
- 850 km²
- 48 kilometres by 32 kilometres of largo
- São Tomé is the most mountainous Santomean island
- 33,600 inhabitants
- Agua Grande is the largest Santomean city
- Príncipe:
- 142 km²
- 16 kilometres by 6 kilometres
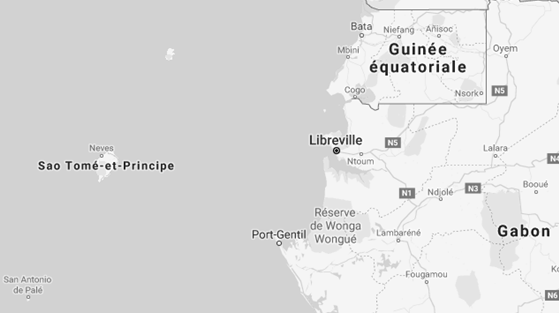
São Tomé and Príncipe is relatively close to the shores of:
- Gabon: 239 kilometres
- Equatorial Guinea: 350 kilometres
- Cameroon
- Nigeria
- Santomean Population density: 187 inhabitants/km²
- Area of São Tomé and Príncipe: 1,000 km² (one of the smallest African countries)
- 30% of the Santomean area are natural parks
- Climate of São Tomé and Príncipe: equatorial
- Peak of São Tomé: 2,024 meters
- São Tomé and Príncipe is a democratic and pluralistic parliamentary republic
- São Tomé and Príncipe obtained its Independence from Portugal in 1975
- Calling code of São Tomé and Príncipe: 239
- Santomean code top-level domain: .st
- Currency of São Tomé and Príncipe: Dobra
- National Museum of São Tomé and Príncipe
Provinces of São Tomé and Príncipe
The two provinces of São Tomé and Príncipe are (between parenthesis capital/population in thousands of people/area):
São Tomé province
- The capital is São Tomé (53,300 inhabitants)
- São Tomé province has six districts:
- Água Grande (51.886 inhabitants)
- Cantagalo
- Caué
- Lembá
- Lobata
- Mé-Zóchi
Príncipe province (self-governed)
- The capital is San Antonio (5,400 inhabitants)
- District of Pagué
Religions in the Democratic Republic of São Tomé and Príncipe:
-
Christianity (95%
of the Santomean population)
- Catholicism (80% of the Santomean population)
- Protestantism (15%)
- Islam (3%)
- African Traditional Religions
Languages of São Tomé and Príncipe
- The official language of São Tomé and Príncipe is Portuguese
- Saotomense and Príncipense are also official languages
- Creole languages: Angolar and Forro
History of São Tomé and Príncipe
- São Tomé and Príncipe was uninhabited until the European arrival
- 1471: João de Santarém (Portugal) discover São Tomé
- 1493: arrival of Spanish Jews
- 15th century: installation of Portuguese colonists
- African slaves importation
- 1534: creation of the Diocese of São Tomé and Príncipe
- 1951: Overseas Province (Portugal)
- 1975: independence (Portugal)
- Marxist regime (Manuel Pinto da Costa)
- 1990: multiparty
- 2003: coup d'etat
Higher Education in São Tomé and Príncipe
Ministry of Education, Culture and Science of the Democratic Republic of São Tomé and Príncipe.
Santomean Universities:
- University of São Tomé and Príncipe
- University Institute of accounting, administration and IT (IUCAI)
- Lusíada University (Portugal)
São Tomé and Príncipe is not a member of the African and Malagasy Council for Higher Education (CAMES)
 São Tomé y Príncipe
São Tomé y Príncipe
 São Tomé-et-Principe
São Tomé-et-Principe
 São Tomé e Príncipe
São Tomé e Príncipe


 Tweet
Tweet