Foreign Trade and Transport in Equatorial Guinea, Oil
Equatorial Guinea, Malabo, Bata, Petroleum (Foreign Trade, Business)

Equatorial Guinea is a Central African country
- Equatorial Guinean Population: 1.2 million inhabitants
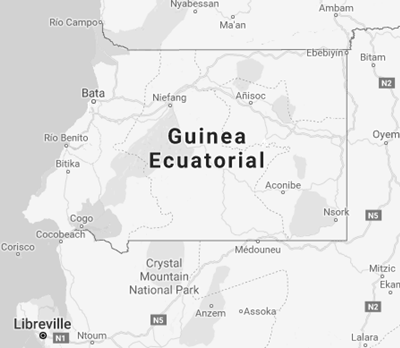
- Malabo (Bioko Island, insular Guinea) is the capital of Equatorial Guinea
- Bata is the Equatorial Guinean economic capital and the largest city
- Equatorial Guinea is the third largest oil producer in Sub-Saharan Africa (90% of the Equatorial Guinean exports)
- Equatorial Guinea is a flag of convenience
- Equatorial Guinea is the richest country per capita in Africa.
- Equatorial Guinea has one of the worst results regarding human rights in the world
- Currency of Equatorial Guinea: the CFA Franc (XAF)
- The main religions are Catholic Christianity (81% of the population) and the African Traditional Religions
- The Continental Equatorial Guinea (66% of the territory) share borders with Cameroon (189 kilometres) and Gabon (350 kilometres)
- The island of Annobón belongs to Equatorial Guinea

Transport and Logistics in Equatorial Guinea

- In Equatorial Guinea, there are 2,880 kilometres of Roads, most of which have not been paved
- National Road 2 (Cameroon): Ambam (Cameroon, Yaoundé, Douala) - Gabon (Libreville, Oyem) - Equatorial Guinea.
- During the rainy season, roads are often impassable without a vehicle with four-wheel drive.
- Project to improve the paved roads of Malabo in Luba and Riaba
- Project: Mongomo bridge (Gabon) -Bata
- Bata-Mbini Bridge: the longest African bridge
- Project: Equatorial Guinea Network (continental) - Cameroon - Gabon
Ports of Malabo, Bata and Luba Free Port
- President Obiang Nguema International Airport
- Bata International Airport
 Equatorial Guinea
Equatorial Guinea


More information: International Trade and Business in Equatorial Guinea, at EENI Global Business School Website.

- Population density of Equatorial Guinea: 26.4 inhabitants/km²
- Equatorial Guinea is a Presidential Republic
- Area of Equatorial Guinea: 28,051 km² (Equatorial Guinea is one of the smallest African states)
- Equatorial Guinea obtained its Independence from Spain in 1968
- Calling code of Equatorial Guinea: 240
- Code top-level domain of Equatorial Guinea: .gq
The ten regions of Equatorial Guinea are (in brackets: the capital):
- Insular region (Malabo). Islands of Bioko and Annobón
- Annobón (San Antonio of Palé)
- Bioko North (Rebola). Districts:
- Malabo
- Baney
- Bioko-South (Luba). Districts:
- Luba
- Riaba
- Continental region (Bata)
- Centre-South (Evinayong). Districts:
- District of Evinayong
- District of Akurenam
- Niefang
- Kié-Ntem (Ebebiyin). Districts:
- Mikomeseng
- Nsoc Nsomo
- District of Ebebiyín
- Littoral (Bata). Districts:
- Bata
- Cogo
- Mbini
- Wele-Nzas (Mongomo). Districts:
- Mongomo
- Nsork
- District of Awithibe
- District of Añisoc
- District Oyala
- Centre-South (Evinayong). Districts:

Trade and Business Organisations (Equatorial Guinea)
- Central African Economic and Monetary Community (CEMAC)
- Economic Community of Central African States (ECCAS)
- OHADA
- Bank of Central African States (BEA)
- OIF
- Organisation of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC)
- African Union
- AUDA-NEPAD
- Economic Commission for Africa
- African Development Bank
Equatorial Guinean ethnicities:
99% of the population of Equatorial Guinea is Bantu:
- Fang (72% of the population of Rio Muni)
- Bubi (15% of Bioko).

Religions and Global Business -
Religious diversity
Religions in the Republic of Equatorial Guinea
- Christianity
- Catholics
- Protestants
- African Traditional Religions
Languages of Equatorial Guinea
The three official languages of Equatorial Guinea are:
- Spanish (national Equatorial Guinean language, 88% of the population)
- French (since 1997, compulsory in secondary)
- Portuguese (since 2011)
Fang language is the main language of the continental territory of Equatorial Guinea, Fang has more than a million speakers, which almost 300 thousand are Equatorial Guineans. It is a Bantu language.
Bubi language is the main language of the island of Bioko. It is a Bantu language.
Benga is spoken on the south coast of the Muni River among Ndowé language fang is the main language of the continental territory of Equatorial Guinea, has more than a million speakers, which almost 300 thousand are Equatorial Guineans. It is a Bantu language.
History of Equatorial Guinea
- 30,000 BC: human remains in the Littoral province (Mossumu)
- 3,000 BC: hunter-gatherers in Bata
- 1469: the Portuguese arrive
- 1778: colonization (Spain): Spanish Guinea (Treaty of San Ildefonso, Treaty of Pardo)
- 1856: official foundation of Spanish Guinea for Spain
- 1958: autonomous government
- 1959: the Spanish territories of the Gulf of Guinea acquire the status of Spanish Overseas Provinces
- 1968: independence of Equatorial Guinea from Spain
Higher Education in Equatorial Guinea
- National University of Equatorial Guinea (Malabo)
Equatorial Guinea is a member of the African and Malagasy Council for Higher Education (CAMES) and the Francophone University Agency (AUF)
 Guinea Ecuatorial
Guinea Ecuatorial
 Guinée équatoriale
Guinée équatoriale
 Guiné Equatorial
Guiné Equatorial


 Tweet
Tweet