Foreign Trade in South Sudan, Juba, Dinkas
Business in South Sudan (Foreing Trade) Juba, Dinka, Malakal, Wau

The Republic of South Sudan («the youngest nation in the world» or «The Nilotic Republic») is an East African landlocked country
- Juba is the economic, political and administrative capital of South Sudan and the largest South Sudanese city (300,000 people)
- Largest cities of South Sudan: Juba (political capital), Malakal, Wau, Yambio, Yei, Aweil, Gogrial, Rumbek, Bor and Torit
- South Sudan is one of the poorest and most undeveloped countries in the world (fragile State)
- Main South Sudanese economic activity: agriculture, transport
- Main agricultural products: cotton, peanuts, sorghum, millet, wheat, corn, Arabic gum and sugar cane.
- Wood exports
- Beverage Factory of South Sudan (subsidiary of SABMille)
- Main mineral resources in South Sudan: oil, iron ore, copper, chromium ore, zinc...
- Oil: 60% of the South Sudanese GDP
- South Sudan has the third largest oil reserve in Sub-Saharan Africa
- Hydroelectric power generation (White Nile)
- Currency of South Sudan: South Sudanese pound
- Borders of South Sudan: Ethiopia (Adama, Awasa, 883 kilometres), Kenya (232 kilometres), Uganda (435 kilometres), the Central African Republic (682 kilometres), the DR Congo (628 kilometres) and Sudan (1 937 kilometres)
- Northern Transport Corridor
- Nearest port to South Sudan: Port of Mombasa (Kenya)

 South Sudanese Students from South Sudan
South Sudanese Students from South Sudan


More information: International Trade and Business in South Sudan, at EENI Global Business School.

Trade and Business Organisations (South Sudan)
- East African Community (EAC)
- United States-East African Community Agreement
- Intergovernmental Authority on Development (IGAD)
- Common Market for Eastern and Southern Africa (COMESA)
- U.S.-COMESA Agreement
- COMESA-EAC-SADC Agreement
- Nile Basin Initiative
- Conference on the Great Lakes Region
- Great Lakes Region

- African Development Bank
- African Union
- AUDA-NEPAD
- Economic Commission for Africa

- South Sudan is a Presidential Constitutional Federal Republic
- South Sudan obtained the Independence from Sudan in 2011 (History of South Sudan)
- 2013- until today: civil war and ethnic violence
- More than two million of South Sudanese dead and more than four million displaced
- Border disputes with Sudan
- Calling code: 211
- Country code top-level domain: .ss
Official language of South Sudan: English.
- More than 60 indigenous languages in South Sudan
- Most spoken South Sudanese languages: Dinka, Nuer, Bari and Zande.

Religions and Global Business -
Religious diversity
Religions in South Sudan:
- Christianity
-
African Traditional Religions
- Dinka believe in one God (Nhialic) who speaks through the spirits
- South Sudanese population: 12.2 million people
- Population density of South Sudan: 13.33 inhabitants / km²
- Area of South Sudan: 644,329 km²
- Main South Sudanese rivers: White Nile and its tributary, the Bahr el-Ghazal
- South Sudan comprises the vast marshy area of the Sudd (Bahr al Jabal) formed by the White Nile
- Mont Kinyeti: 3,187 meters
- Climate of South Sudan: tropical
The 28 Federated States of South Sudan are (2015 reform) (State / capital):
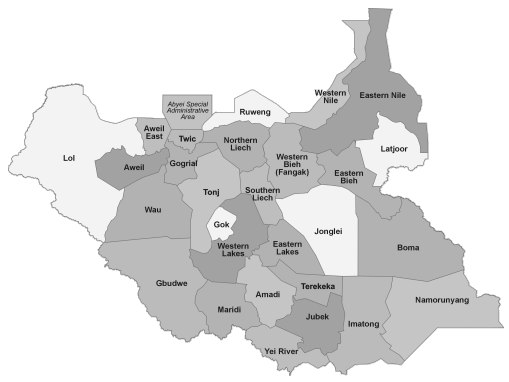
Bahr el Ghazal Region
- Aweil / Aweil
- East Aweil / Wanyjok
- Gogrial / Kuajok
- Gok / Cueibet
- Western Lakes/ Rumbek
- Eastern Lake / Yirol
- Lol / Raga
- Tonj / Tonj
- Twic / Mayen Abun
- Wau / Wau
Equatoria Region
- Amadi / Mundri
- Gbudwe / Yambio
- Imatong / Torit
- Jubek / Juba
- Maridi / Maridi
- Namorunyang / Kapoeta
- Yei River / Yei
- Terekeka / Terekeka
Upper Nile Region
- Western Bieh / Ayod
- Oriental Bieh / Akobo
- Boma / Pibor
- Jonglei / Bor
- Latjoor / Nasir
- Northern Liech / Bentiu
- South Liech / Leer
- Western Nile/ Kodok (formerly Fachoda)
- Eastern Nile / Malakal
- Ruweng / Panriang
Main South Sudan ethnic groups: Nilotic peoples (Nilotic Republic)
In South Sudan live more than 62 South Sudanese ethnic groups.
Dinka (Nilotic group) is the most important group in South Sudan
- 40% of the population of South Sudan
- Historical regions of Bor and Bahr el Ghazal
- Dinka speak Dinka language (Nilo-Saharan)
- Organization by independent clans
Nuer (Nilotic group)
- Nuer are the second most important group in South Sudan
- 16% of the South Sudanese population
- Nuer people are an important minority in the Great Nile region, formed by the Upper Nile, Jonglei and South Sudan.
- Nuer speak Nuer language
Higher Education in South Sudan
 Sudán del Sur
Sudán del Sur
 Soudan du Sud
Soudan du Sud
 Sudão do Sul
Sudão do Sul


 Tweet
Tweet