Foreign Trade and Transport in Benin, Cotonou
Business in Benin: Cotonou, Porto-Novo, Abomey, Parakou, Djougou, Fon

Benin is a West African country
- Total Beninese population: 10.7 million inhabitants
- The political capital of Benin is Porto-Novo (Xogbonou in Goun)
- The economic capital of Benin is Cotonou
- The Beninese historical capital is Abomey
- Abomey-Calavi is the second most populated Beninese city (Atlantic Department)
- Kétou (Plateau Department)
- Parakou (Borgou Department)
- Djougou (Donga Department)
- The Beninese democracy is very consolidated
- Benin has an important informal Cross-Border trade with Nigeria
- The Currency of Benin is the CFA Franc
- Benin share borders (2,123 kilometres) with Burkina Faso (386 kilometres), Nigeria (809 kilometres, Lagos), Niger (277 kilometres) and Togo (651 kilometres)

Transport and Logistics in Benin
Access to the Dakar-Lagos Transport Corridor
Railway loop: Benin-Niger-Burkina Faso-Ivory Coast
- Malanville, Kandi, Parakou, Porto-Novo, Cotonou
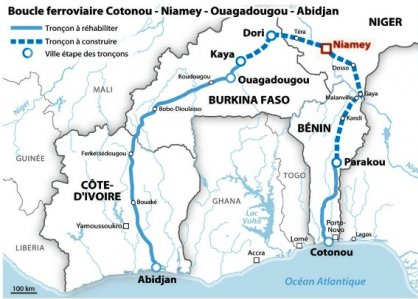
Source: Commodafrica
Axes:
- Route: Ouagadougou (Burkina Faso)-Cotonou (Benin)
- Route RNIE2: Cotonou, Porto-Novo, Parakou, Kandi, Niger

 Benin
Benin


More information: International Trade and Business in Benin, at EENI Global Business School Website.
- Official language of Benin: French
- African languages of Benin are Fon (44% of the Beninese population), Yoruba (14%), Goun, Mina, Adja and Bariba
- Total Beninese area: 114.763 km²
- Calling code of Benin: 229
- Beninese code top-level domain: .bj
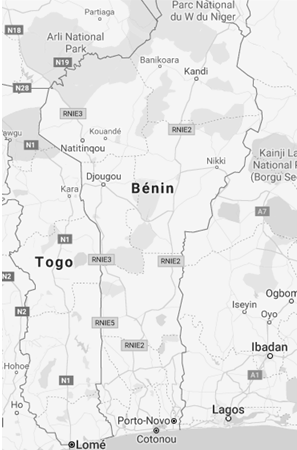
The Republic of Benin is composed of twelve departments:
- Alibori
- Atacora
- Atlantic
- Borgou
- Collines
- Couffo
- Donga
- Littoral (Cotonou)
- Mono
- Ouémé
- Plateau
- Zou

Trade and Business Organisations (Benin)
- West African Economic and Monetary Union (WAEMU)
- U.S.-WAEMU Agreement
- Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS)
- Niger Basin Authority
- Community of Sahel-Saharan States (CEN-SAD)
- OHADA
- Global System of Trade Preferences
- African Union
- AUDA-NEPAD
- Economic Commission for Africa
- African Development Bank

Religions and Global Business -
Religious diversity
Religion in Benin:
- Sunni Islam (28% of the Beninese population)
- African Traditional Religions
- Voodoo
- Christianity
- Benin is a Secular State (Constitution of 1990)
Main Beninese Ethnicities:
- Fon (39% of the Beninese population, South of Benin)
- Adja (15% of the Beninese population)
- Yoruba (12%)
- Bariba (9%)
- Other ethnicities: Fula (7%), Batammariba and Dendi
The leopard in the Kingdom of Benin is the animal related to the King (Oba) (Source: Jesús Arjona Muñoz, African Art Exhibition: “The Animal, A Sacred Symbol”)

History of Benin
- 14th Century: Kingdoms Aja-Ewé
- 16th Century: Bariba Kingdoms and Kingdom of Nikki (North of Benin)
- Yoruba Kingdoms (East of Benin)
- Kingdom of Shabê-Okpa and Kingdom of Kétou
- 1645: Kingdom of Dahomey
- Independence from France: August 1960 (Republic of Dahomey)
- 1975: People's Republic of Benin (Communist, Mathieu Kérékou)
- 1990: Republic of Benin
- World Heritage:
- The Royal Palaces of Abomey
- The Complex W-Arly-Pendjari
Higher Education in Benin
2012: LMD System (Bachelor, Master, Doctorate) - Beninese Ministry of Higher Education and Scientific Research
100,000 Higher Education Students
- University of Abomey-Calavi
- University of Parakou
- National University of Sciences, Technologies, Engineering and Mathematics (UNSTIM) - Cotonou
- National University of Agriculture (UNA) - Kétou
Benin is a member of the African and Malagasy Council for Higher Education (CAMES)


 Tweet
Tweet

