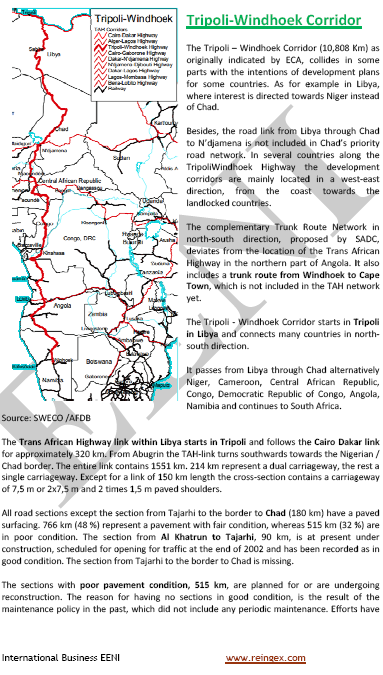
Foreign Trade and Transport in Libya, Tripoli, Tobruk
Business the State of Libya (civil war), Petroleum, Tripoli, Benghazi

Libya is a Maghrebian country (north-west Africa)
- دولة ليبي in Arabic
- ⵍⵉⴱⵢⴰ in Berber (Amazigh)
- Population of Libya: 6.3 million inhabitants
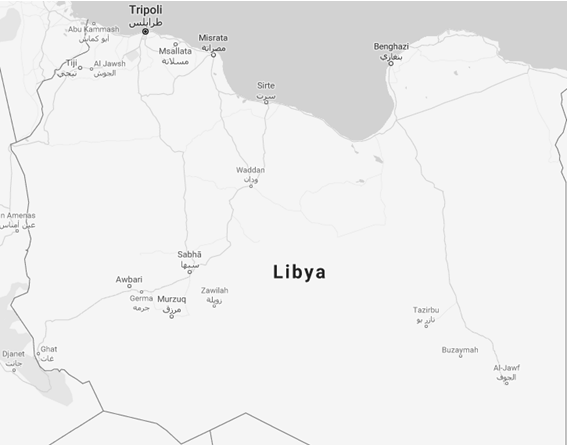
- Tripoli is the capital (General National Congress) and the largest Libyan city
- Main Libyan cities: Tripoli, Benghazi, Misrata, El-Beida, Al Khums, Zawiya, Ajdabiya, Sabha, Sirte and Tobruk (Council of Deputies)
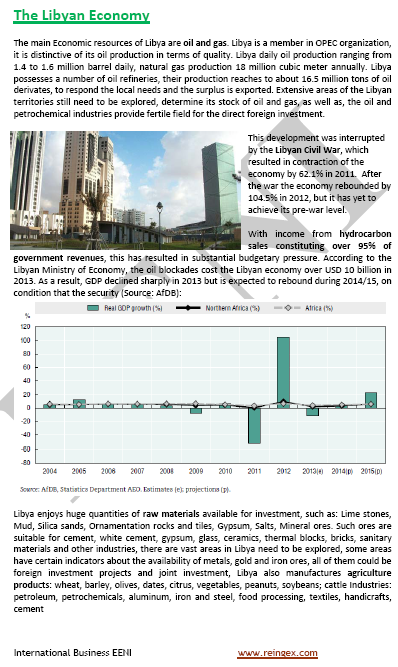
- Main mineral resources of Libya: petroleum and gas
- 50% of the Libyan GDP
- 97% of the Libyan exports
- Libya has the largest tested oil reserves in Africa
- Libya is a high-middle-income economy (World Bank)
- 17% of the Libyan active population works in agriculture
- Great artificial river (network of the water pipes built by Gaddafi to irrigate the Sahara desert)
- Libya imports 90% of its cereal consumption needs
- The headquarters of the Community of Sahel-Saharan States (CEN-SAD) are in Tripoli
- Libya share borders with Algeria (982 kilometres), Egypt (1,115 kilometres), Niger (354 kilometres), Sudan (383 kilometres), Chad (1,055 kilometres, Abéché) and Tunisia (459 kilometres)
Logistics and Transportation in Libya
Chad - Libya Railway

Trade and Business Organisations (Libya)
- Arab Maghreb Union (AMU)
- Community of Sahel-Saharan States (CEN-SAD)
- Common Market for Eastern and Southern Africa (COMESA)
- U.S.-COMESA Agreement
- COMESA-EAC-SADC Tripartite Free Trade Agreement
- Euro-Mediterranean Partnership
- Islamic Development Bank
- Organisation of Islamic Cooperation (OIC)
- Economic and Social Commission for Western Asia
- Arab League
- Organisation of oil exporting countries (OPEC)
- Greater Arab Free-Trade Area
- Global System of Trade Preferences
- Agadir Agreement
- African Union
- AUDA-NEPAD
- Economic Commission for Africa
- African Development Bank
 Libyan Students
from Libya
Libyan Students
from Libya


More information: International Trade and Business in Libya, at EENI Global Business School Website.
- Libya is on the Mediterranean coast of North Africa
- South of Libya: the Sahara desert
- Tibesti massif: 2,200 meters
- area of Libya: 1.8 million km²
- Libya has 2,000 kilometres of the Mediterranean coast
- Libya is the fourth largest African Country
- The three historical regions are Tripolitana, Fezan and Cyrenaica
- The 22 districts (baladiyat) of Libya are Nuqat al Khams, Zawiya, Jafara, Tripoli, Murqub, Misrata, Sirte, Benghazi, Marj, Jabal al Akhdar, Derna, Tobruk, Nalut, Jabal al Gharbi, Wadi al Shatii, Jufra, Al Wahat, Ghat, Wadi al Hayaa, Sabha, Murzuq and Kufra
- Official languages of Libya: Arabic and Tamazight
- Main Libyan ethnic group: Berbers
- The majority of the Libyan population is considered Arab and Arabophone
- 90% of the Libyan Arab population is Arabized Berber
- Berbers are a minority
- Religion: Sunni Islam (96% of the Libyan population)
- Libyan Country code top-level domain: .ly
- Calling code of Libya: 218
- Currency of Libya: Libyan Dinar
Recent history of Libya
- 1947: Independence (Italy)
- 1947 - 1951: British and French supervision
- 1969: Coup d'etat of Muammar Gaddafi
- 1977: Libyan Arab Jamahiriya
- 2011: Libyan revolution
- Second Libyan civil war (since 2014)
- It will take at least ten years to rebuild the infrastructure of Libya
Provisional Government
- In the second Libyan civil war, active since 2014, two authorities
initially claimed to govern Libya:
- The Council of Deputies in Tobruk
- The General National Congress 2014 in Tripoli
- 2015: unified agreement of the national government with the support of the UN
- Some parts of Libya remain outside of government control, with several Islamists, rebel and tribal militias administering certain areas
Higher Education in Libya
- University of Benghazi
- University of Libya
- University of Tripoli
- Asmarya University of Islamic Sciences
- Azzaytuna University
- Al-Mergib University
- Misurata University
- Omar Al-Mukhtar University
- SabratUniversity
- SabUniversity
- Syrte University
- Al Zawiya University
- Al-Arab University of Medicine
- University of Al-Fateh


 Tweet
Tweet


